Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease. The main clinical manifestations include joint swelling, destruction of articular cartilage and joint dysfunction. So far, there is no ideal drug to cure rheumatoid disease. There are about 5 million RA patients in China and if they receive improper treatment, 30% of patients will be led to joint disability within 2 years. Therefore, identifying drugs that can target the pathological characteristics of rheumatoid disease is a hot research topic in anti-RA therapy.
The research team led by Professor Liu Liang who is an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering and president of the Macau University of Science and Technology (M.U.S.T.), has long been engaged in clinical research and new drug discovery from traditional Chinese medicine, and has achieved a series of promising results. Recently, the team found that the synovial cells from RA patients were characterized by extremely high level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial superoxide. Based on these findings, they cooperated with Professor Yuan Zhen from University of Macau to develop a ROS-responsive nano-delivery system to specifically transport drug to target site with inflammation and berberine was applied as a tool drug (BPseP-berberine). It can effectively promote the accumulation of berberine in RA tissues, especially in the MTX resistant RA cell, and thereby enhance the therapeutic effect. The experiment of arthritis animal model also demonstrated that the effect of BPseP-berberine, in anti-arthritis and joint protection, remarkably increased more than 10 times than that of berberine. Therefore, using the ROS-responsive nano-delivery system can significantly lower the dosage of drugs and consequently reduce their toxicity and side effects.
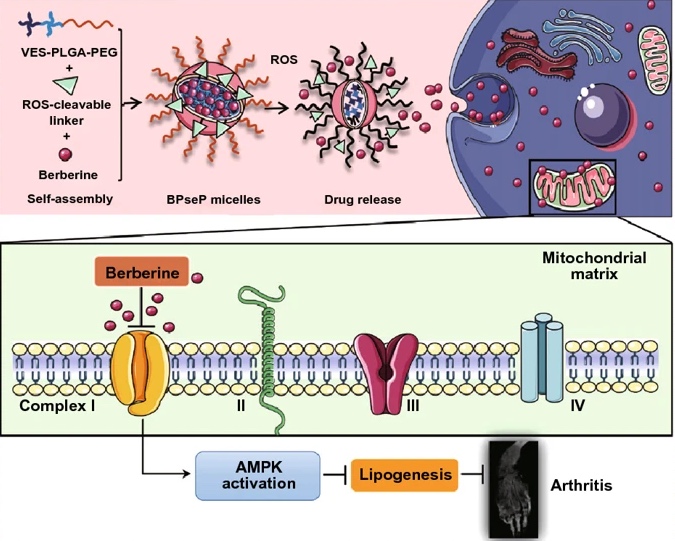
ROS-responsive berberine micelles significantly inhibits arthritis by targeting inflammatory cells and mitochondria
The ROS-responsive delivery system represents a new strategy for the development of highly effective and low-toxic innovative drugs to treat RA, and possesses broad application prospects. The results were published in Nano-Micro Letters, (2019 impact factor: 9.043; immediate impact factor: 13; https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-0410-x). Professor Liu Liang and Yuan Zhen are the corresponding authors; Assistant Professor Fan Xing-Xing from the State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine of M.U.S.T. and Dr. Xu Meng-Ze from University of Macau are co-first authors; Associate Professor Elaine Lai-Han Leung and Dr. Cai Jun from M.U.S.T. are co-authors.





